As concerns for climate change intensify, the building and construction industry faces higher sustainability standards from planners and regulations. This is pushing for new and creative methods to meet client demands.
Key factors driving sustainability in construction
Environmental impact: Besides causing the loss of wild habitats, the building sector generates approximately 100 billion tonnes of waste through construction, renovation, and demolition worldwide, with 35% ending up in landfills. Globally, buildings are currently responsible for 39% of energy-related carbon emissions.
Government regulations: Governments worldwide have implemented more stringent building regulations to encourage sustainable construction practices, including the Construction Products Regulation (CPR) and the European Green Deal. Countries like the UK and the US have also set ambitious targets towards this goal in support of the Paris Agreement.
Green building certifications: The rise in various green building certification systems, such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method), has incentivized construction companies to design and construct greener buildings for the future.
Cost control: Due to the rising cost of raw materials, those in charge of construction projects must strategically plan and manage their projects using the most cost-effective products.
Ultimately, adopting innovative sustainable construction practices is the key to significantly reducing our environmental impact. However, to help ensure long-term sustainability, it is crucial to tackle the detrimental effects of mold on building structures.

Mold growing on tile grout
The perils of mold growth affecting sustainable construction
Mold growth poses a significant threat to building materials, leading to premature degradation. In high-moisture environments, such as bathrooms, kitchens, roofs, and basements, mold can proliferate rapidly on surfaces like walls, ceilings, and insulation. When left unaddressed, mold weakens structural integrity and releases harmful airborne spores, impacting indoor air quality and the well-being of occupants.
Mitigating mold with antimicrobial technology
Incorporating antimicrobial technology during manufacturing provides a proactive defense against the growth of bacteria, mold, and mildew. The antimicrobial agents operate at a cellular level, disrupting the microbial life cycle and preventing surface colonization. Consequently, building materials with built-in antimicrobial protection remain cleaner, fresher, and more durable.
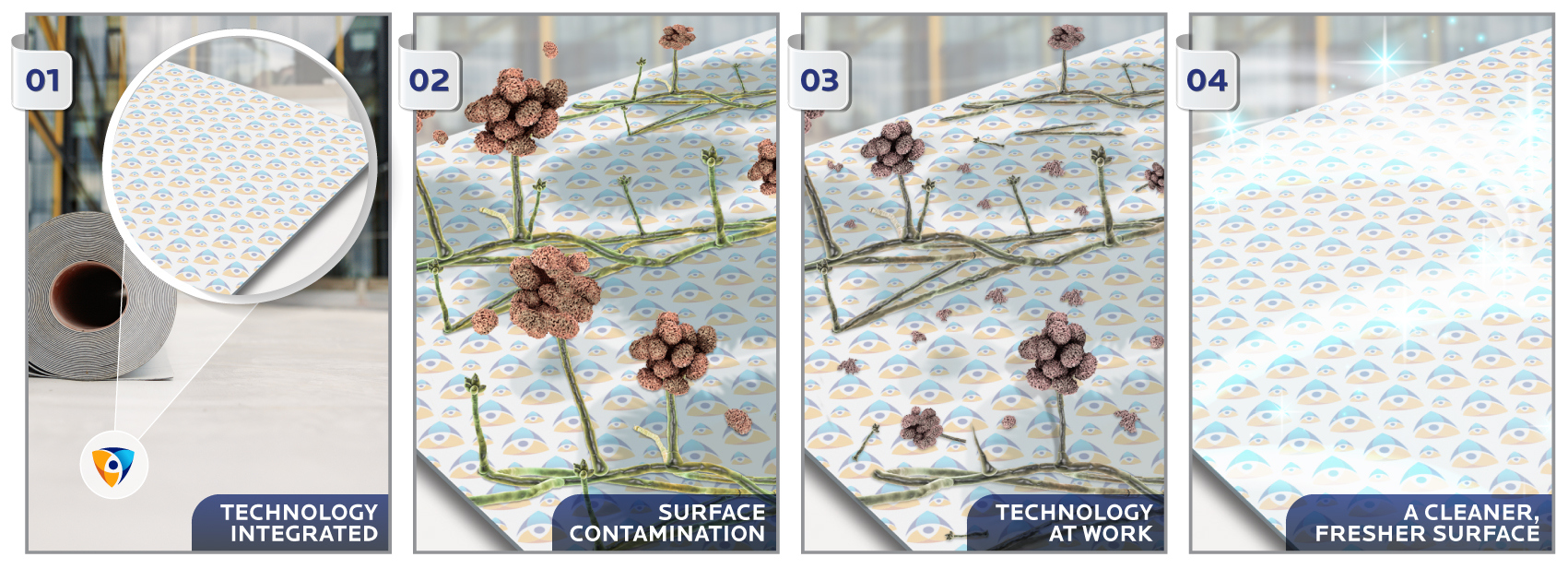
Microban technology: Solutions for sustainable construction
The use of antimicrobial technology contributes to sustainable construction in the following ways:
Improved indoor air quality
The growth of mold can negatively impact the quality of indoor air in constructed environments. However, using antimicrobial building materials can prevent mold from proliferating on surfaces and in HVAC filtration systems. This helps to promote cleaner air, healthier indoor environments and enhances the well-being of occupants.
Lower landfill loading
Durable building materials have a longer lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacement or repairs. When materials last longer, less waste is generated over time, reducing the demand for new materials and the associated environmental impact of manufacturing and transportation.
Water and energy efficiency
Enhancing surfaces and finishes with antimicrobial coatings keeps them cleaner and fresher for longer, resulting in less cleaning and maintenance when compared to untreated counterparts. This translates to water and energy savings over the building's lifespan. In addition, using fewer chemicals for cleaning helps to reduce the overall impact on the environment.
Longer functional life
Antimicrobial technologies can be incorporated into various structural materials, coatings, and paints at the point of manufacture, without compromising performance or compliance with building specifications. The benefits include increased building durability, lower repair costs, and reduced consumption of resources and energy. Furthermore, these materials also help the construction industry meet the demands of environmentally responsible homeowners and governments, ultimately contributing to the sustainability of our planet.
What antimicrobial technologies are compatible with construction materials?
Microban offers a variety of antimicrobial technologies to create more sustainable building materials, including our latest additions of metal-free chemistries:

Ascera™ is an antimicrobial technology, inspired by nature*, designed for solvent-based coatings and polymer applications.

MicroGuard™ is a range of metal-free antifungal technologies for polymeric applications. It is also a sustainable alternative to arsenic-based formulations.

LapisShield™ is a heavy-metal-free antimicrobial technology that offers improved quality and stability for water-based coating systems.


